The Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) recent move to join Project Nexus, a multilateral initiative to enhance cross-border retail payments, is a significant step forward. By collaborating with the Bank for International Settlements’ Innovation Hub, RBI aims to interconnect domestic fast payment systems (FPS) across ASEAN countries, including Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and India as a founding member. With an expected launch by 2026, this platform will streamline cross-border transactions, making them faster and more cost-effective.
The Association of Southeast Asian Nations, or ASEAN, is a diverse economic community with varying economic systems and growth stages. Brunei, despite its small size, relies heavily on petrol and oil exports. Cambodia and Laos are emerging economies, focusing on clothing manufacturing and agriculture. Indonesia, the largest economy in ASEAN, boasts a wide range of exports such as textiles, coal, and palm oil. Malaysia’s economy is strong and varied, benefiting from oil, gas, and electronics. Myanmar, an emerging economy, shows promise with its natural resources and agricultural sector.
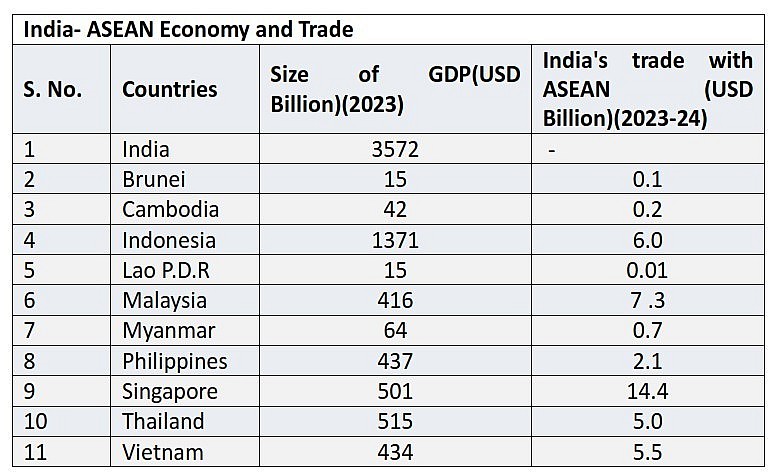
India’s trade relations with ASEAN countries highlight economic interdependencies and mutual benefits. The table below offers a glimpse of the GDP and trade figures of selected ASEAN countries with India for the fiscal year 2023-24:
 |
The Philippines has a strong service industry, particularly in business process outsourcing. Singapore, a financial hub, excels in technology, banking, and finance exports. Thailand’s well-rounded economy is driven by robust tourism, automobile, and electronics sectors. Vietnam is accelerating its industrialization, with electronics and garments as key exports.
Project Nexus’ multilateral approach expands the scope of international cooperation while enhancing the bilateral advantages of India’s Unified Payments Interface (UPI) with each ASEAN member state. This initiative aims to foster commercial and economic ties by facilitating rapid cross-border retail payments. By providing access to more efficient and seamless financial transactions, the platform promotes global economic cooperation and integration. The Nexus platform offers several key advantages:
1. Efficiency: By interconnecting domestic FPSs, the platform ensures swift cross-border payment processing, reducing the time typically required for international transactions. This efficiency is crucial for businesses relying on timely payments for goods and services.
2. Cost Savings: Traditional cross-border payment systems often incur high transaction fees. The Nexus platform aims to reduce these costs, alleviating the financial burden on consumers and making international trade more accessible to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
3. Enhanced Trade Relations: Simplifying and accelerating payment processes will likely encourage more companies to engage in international trade, boosting economic relations between India and ASEAN nations. This could lead to stronger economic ties and increased trade volumes.
4. Financial Inclusion: By offering a user-friendly means of making international payments, the Nexus platform has the potential to attract more individuals into the formal financial system. This inclusivity can drive economic growth in underserved areas.
India’s Trade with ASEAN
India’s trade ties with ASEAN nations reached impressive levels in the fiscal year 2023–2024, underscoring the closeness of their economic relations. For instance, trade between India and Singapore stood at USD 14.4 billion, placing Singapore among India’s top trading partners. Malaysia followed closely with USD 7.3 billion in trade. Thailand and Indonesia also held significant commerce with India, totaling USD 5.0 billion and USD 6.0 billion, respectively.
India primarily exports petroleum products, engineering goods, jewelry and gems, organic chemicals, and pharmaceuticals to ASEAN countries. These exports are vital to India’s industrial and manufacturing sectors. In return, ASEAN nations provide India with substantial imports of technology, machinery, mineral fuels, and edible oils. This dynamic import-export relationship fosters economic interdependence and propels technological and industrial advancement in India.
Singapore, a prominent financial hub, imports large quantities of machinery, pharmaceuticals, and petroleum products from India. Simultaneously, it exports equipment, electronics, and organic chemicals to India, highlighting the mutually beneficial nature of their economic relationship. Malaysia, another key partner, imports pharmaceuticals, machinery, and refined petroleum from India while exporting natural rubber, electronic equipment, and palm oil.
Indonesia and Thailand, with their substantial trade volumes, are pivotal in India’s trade landscape. Indonesia exports coal, palm oil, and organic chemicals to India, while India exports refined petroleum, automobiles, and cereals to Indonesia. Thailand’s exports to India include machinery, electronics, and rubber, and India exports pharmaceuticals, textiles, and chemicals to Thailand.
Vietnam has been a major trading partner, purchasing chemicals, steel, and machinery from India and exporting electronics, textiles, and footwear. The Philippines and Myanmar, despite lower trade quantities, contribute to the diverse commercial landscape by importing and exporting minerals, machinery, and agricultural products.
The launch of the Nexus platform is expected to further strengthen these commercial ties. By improving the efficiency and affordability of cross-border payments, the platform will stimulate increased trade with ASEAN countries by enterprises. This will lead to higher trade volumes and a more integrated economic environment, attracting more capital and fostering conditions conducive to economic growth.
In summary, the Nexus platform represents a transformative step towards enhancing economic cooperation between India and ASEAN nations and modernizing cross-border financial systems. By addressing cost and efficiency concerns through instantaneous retail payments, the platform encourages stronger trade and economic ties. Given the diverse economic systems of ASEAN countries and India’s growing economic prowess, both parties stand to gain significantly, leading to increased economic integration.
The success of the Nexus platform will set a precedent for other regions, showcasing how multilateral cooperation in financial technology can promote international trade and economic progress. It will be essential to monitor the platform’s effects on trade dynamics and economic development to ensure it remains responsive to the evolving needs of consumers and businesses.
ASEAN Village 2017
The ASEAN Village took place for the first time in Ho Chi Minh City to mark the 50th anniversary of the foundation of ASEAN (1967 – 2017) and 22 years of Vietnam’s accession to the bloc (1995 – 2017). The event also highlighted the value of the cultural-economic pillar of the ASEAN Community and affirmed the determination of Ho Chi Minh to become an ASEAN city.
“ASEAN People and Countries” Photo Exhibition
An outdoor photo exhibition, titled “ASEAN People and Countries”, is being held from August 4-11 at Ly Thai To Square in Hanoi. At the exhibition, the 10 most outstanding works by 10 photographers, who are also representatives of 10 ASEAN countries, were awarded trophies with the inscription “ASEAN Photos – 2017” by the organising board.








